学术相关
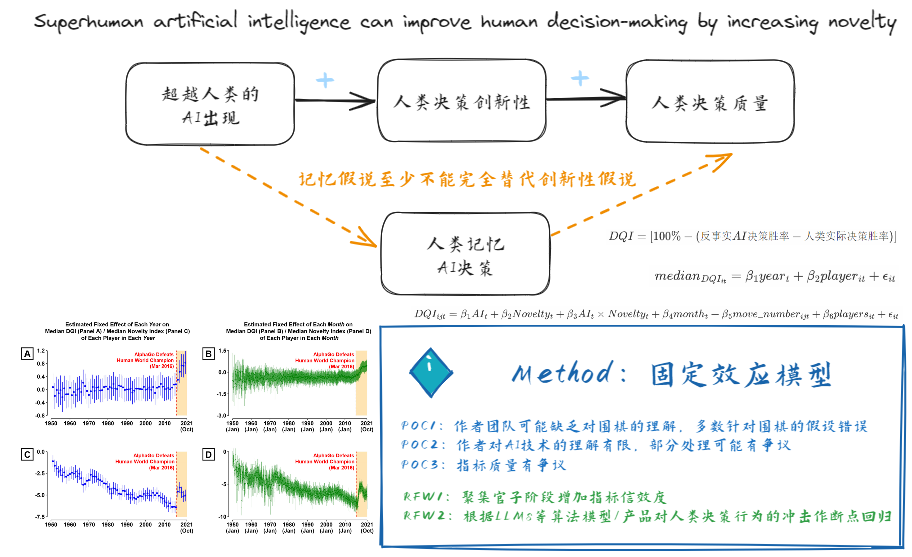
Superhuman artificial intelligence can improve human decision-making by increasing novelty1
| 主题 | Title | Author | Journal | ROF | SPL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 决策、人机协同 | Superhuman artificial intelligence can improve human decision-making by increasing novelty | Minkyu Shin; Jin Kim; Bas Van Opheusden; Thomas L. Griffiths【2023】 | PNAS | 超越人类的AI出现后,人类决策质量提高;超级AI可能通过提高人类的创新性(打破思维桎梏);记忆AI决策不能完全解释人类决策质量提升 | 前人对AI出现后对人类决策质量的影响没有结论;指出创新性可能是关键因素 |
| CPL | GAP | RFW | POC-RPP | IV | DV | Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 很少有研究分析AI出现对人类自身决策水平的影响 | AI对人类自身决策的影响 | 使用更多指标提升稳健性;聚集官子阶段增加指标信效度;拓展领域;根据LLMs或其他算法模型/产品对人类决策行为的冲击作断点回归 | 作者团队可能缺乏对围棋的理解,多数针对围棋的假设错误;作者对AI技术的理解有限,部分处理可能有争议;指标质量有争议 | AI冲击;创新性 | 决策质量指数DQI | 固定效应模型 |
量化因果涌现表明:宏观可以战胜微观2
中国城市间患者流动的影响因素及其网络结构3
业界动态
飞猪旅行:用户出行需求预测
-
Shin, M., Kim, J., Van Opheusden, B., & Griffiths, T. L. (2023). Superhuman artificial intelligence can improve human decision-making by increasing novelty. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 120(12), e2214840120. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2214840120 ↩
-
Hoel, E. P., Albantakis, L., & Tononi, G. (2013). Quantifying causal emergence shows that macro can beat micro. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 110(49), 19790–19795. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1314922110 ↩
-
Ding, J., Yang, C., Wang, Y., Li, P., Wang, F., Kang, Y., Wang, H., Liang, Z., Zhang, J., Han, P., Wang, Z., Chu, E., Li, S., & Zhang, L. (2023). Influential factors of intercity patient mobility and its network structure in China. Cities, 132, 103975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cities.2022.103975 ↩